Creating The Virtual Box VM
Download and Install Oracle VM Virtual Box

Download Ubuntu 22.04 VirtualBox(VDI) Image from Osboxes.org
Note: Extract the content of the downlod downloaded file
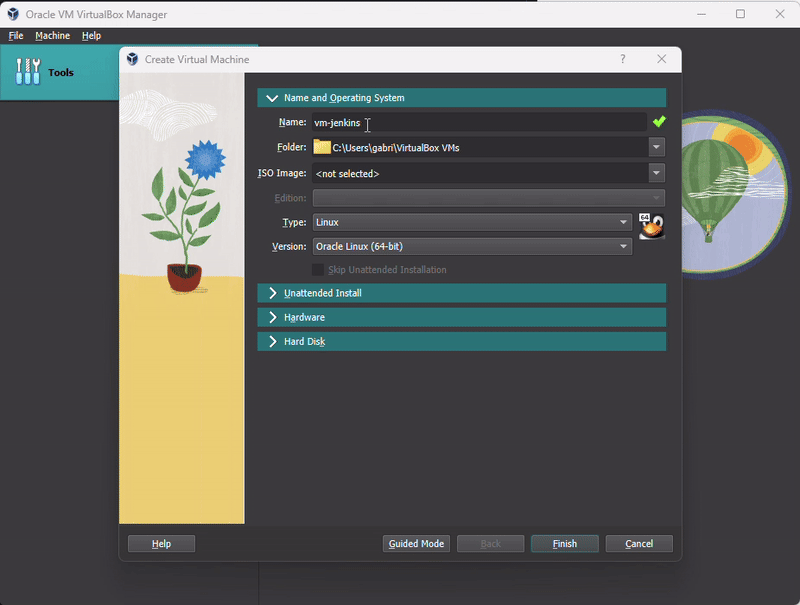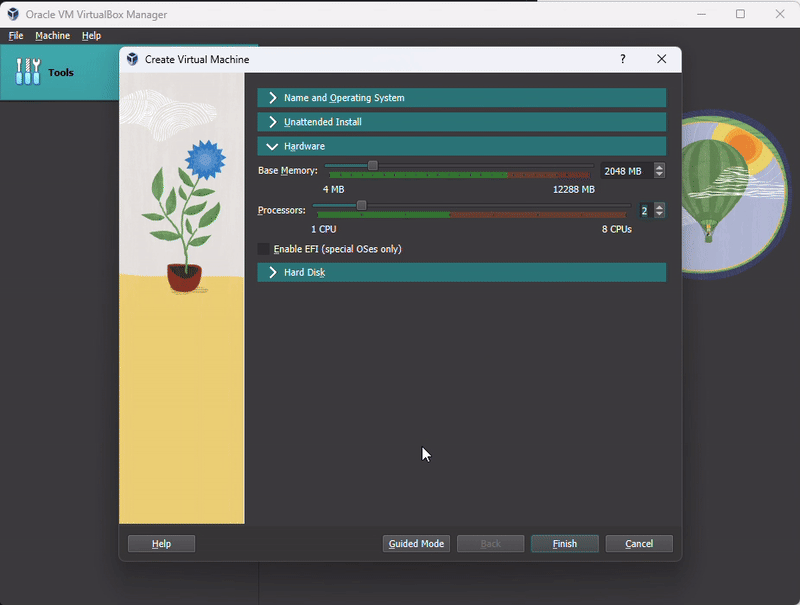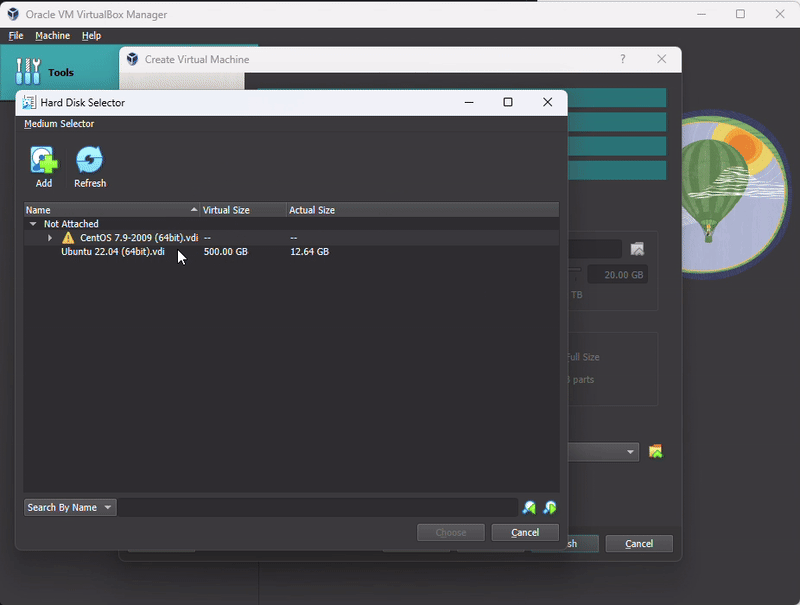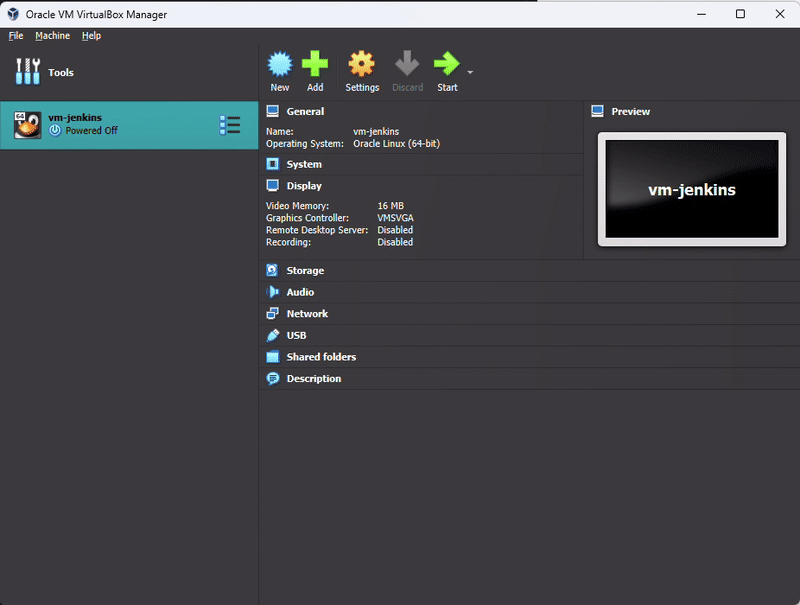
Open Oracle VM Virtual Box application and create new VM
Name: vm-jenkins
Base: Memory 2048
CPU: 2
Use Existing Virtual Hard Disk File: Import the VDI file downloaded earlier
Start Up the VM and Login
Username: osboxes
Password: osboxes.org
Open Terminal and update system
sudo apt update
Installing Jenkins on VM
This is the Debian package repository of Jenkins to automate installation and upgrade. To use this repository, first add the key to your system
sudo wget -O /usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc \
https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable/jenkins.io-2023.key
Then add a Jenkins apt repository entry:
echo deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc] \
https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable binary/ | sudo tee \
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list > /dev/null
Update your local package index, then finally install Jenkins:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install fontconfig openjdk-17-jre -y
sudo apt install jenkins -y
Start Jenkins by using systemctl:
sudo systemctl enable jenkins
sudo systemctl start jenkins
Since systemctl doesn’t display status output, we’ll use the status command to verify that Jenkins started successfully:
sudo systemctl status jenkins
If everything went well, the beginning of the status output shows that the service is active and configured to start at boot(enabled):
Output
● jenkins.service - Jenkins Continuous Integration Server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/jenkins.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Sun 2024-02-25 18:55:21 EST; 10min ago
Main PID: 779 (java)
Tasks: 46 (limit: 2292)
Memory: 273.7M
CPU: 21.993s
CGroup: /system.slice/jenkins.service
└─779 /usr/bin/java -Djava.awt.headless=true -jar /usr/share/java/jenkins.war --webroot=/var/cache/jenkins/war --httpP>
Now that Jenkins is up and running, let’s adjust our firewall rules so that we can reach it from a web browser to complete the initial setup.
Opening the firewall
By default, Jenkins runs on port 8080. We’ll open that port using ufw:
sudo ufw allow 8080
Note: If the firewall is inactive, the following commands will allow OpenSSH and enable the firewall:
sudo ufw allow OpenSSH
sudo ufw enable
Check ufw’s status to confirm the new rules:
sudo ufw status
You’ll notice that traffic is allowed to port 8080 from anywhere:
Status: active
To Action From
-- ------ ----
8080 ALLOW Anywhere
OpenSSH ALLOW Anywhere
8080 (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
OpenSSH (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
Now we will look at how to reach the jenkins vm on the host machine by setting port forwarding.
Setting Up Port Forwarding
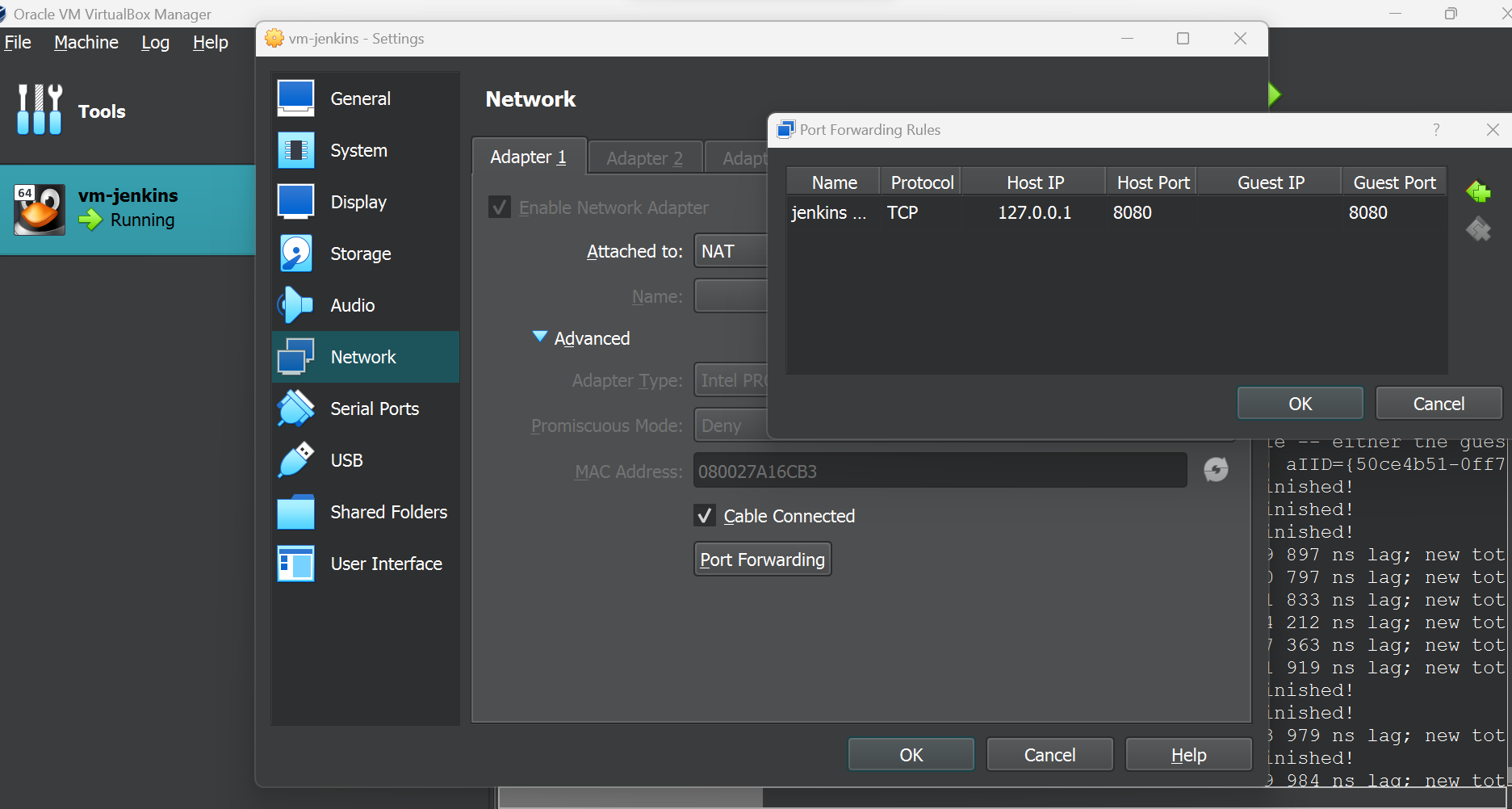
Open VirtualBox VM settings.
Navigate to the NAT network adapter settings.
Click Advanced and then Port Forwarding.
Add a new rule named "jenkins connection".
Set Protocol to TCP.
Enter Host IP as 127.0.0.1 and Host Port as 8080.
Guest Port should also be set to 8080.
Click OK to save the settings.
Setting Up Jenkins
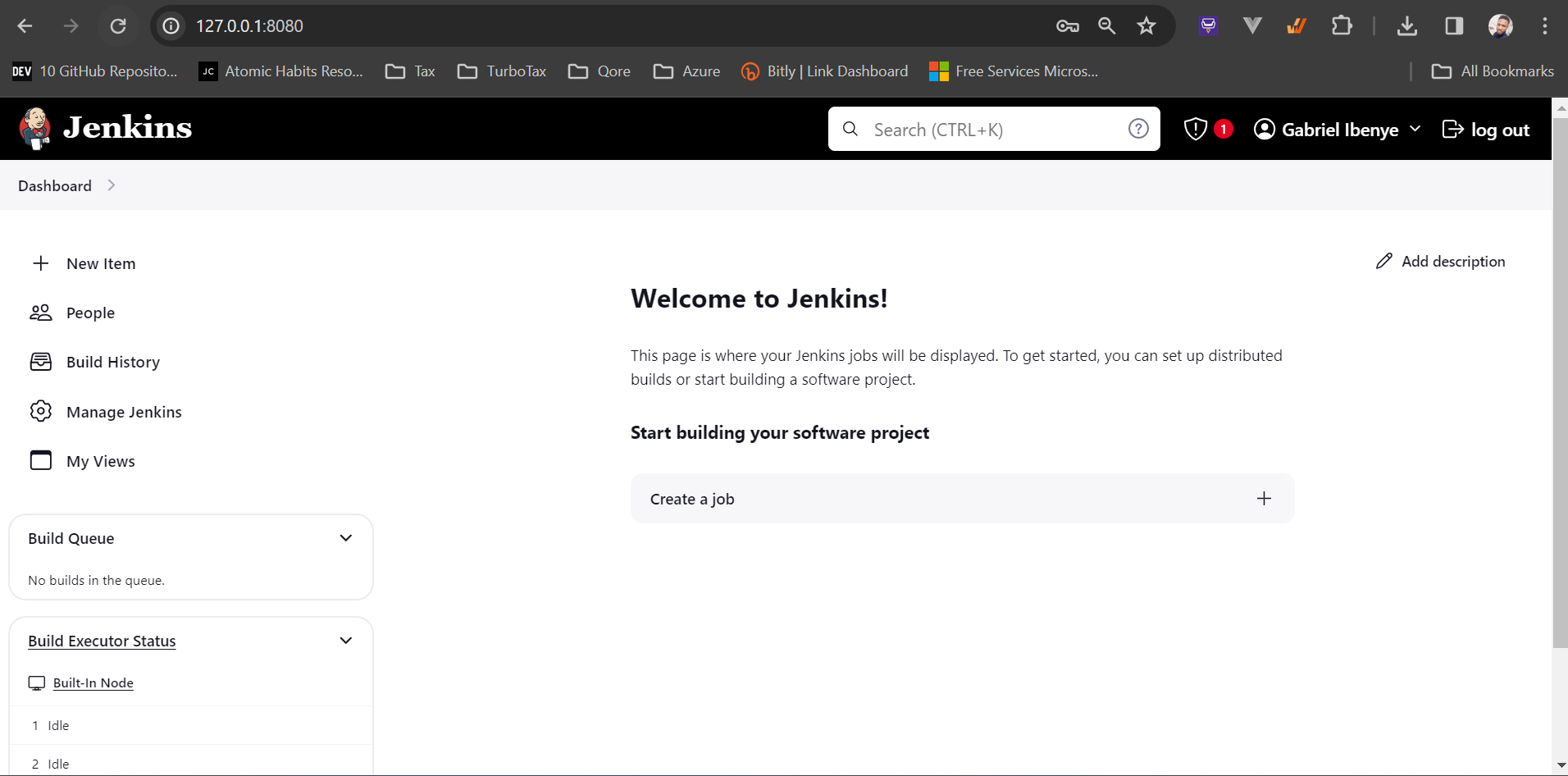
Open your browser and go to 127.0.0.1:8080 to access Jenkins, you will land on the getting started jenkins page:

Use the terminal in your VM and run
sudo cat /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword
Copy the 32-character alphanumeric password from the terminal and paste it into the Administrator password field on the Jenkins page. Then, click Continue. Click on Install suggested plugins Create your admin user Set http://127.0.0.1:8080 as the jenkins URL Click Save and Finish
THE END